By Laura Lagano
Inflammation can be a major contributor to pain, so supporting immune health by using a multifaceted approach can help to relieve discomfort. Lifestyle interventions that integrate cannabis or cannabinoids such as cannabidiol (CBD) with an anti-inflammatory food plan help to lower inflammation, reducing pain.
How cannabis works
Before learning how to tackle pain and inflammation, it is important to understand how cannabis works in the body. There is an entire network made up of cannabinoids, receptors and enzymes called the endocannabinoid system, which works in tandem with various other systems and pathways throughout the body. Endocannabinoids, anandamide (taken from the Sanskrit for “bliss”) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol are cannabinoids that we make ourselves. Endocannabinoids play various roles in regulating cognitive function, mood, hunger, sleep, inflammation and pain. The mechanisms of the endocannabinoid system centre around maintaining homoeostasis, meaning it works to support physiological harmony. The cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 are located within the immune, nervous and digestive systems, and elsewhere throughout the body.
The endocannabinoid system was named after cannabis because researchers discovered it when they were studying the plant. Cannabis contains more than 100 phytocannabinoids (i.e., cannabinoids from plants) that our bodies are innately wired to interact with. Phytocannabinoids such as CBD have demonstrated numerous health benefits, including reducing chronic pain.
CBD is considered the ultimate anti-inflammatory compound. In fact, the US government has a patent on cannabinoids, specifically CBD, as an anti-inflammatory agent.

Pain and inflammation
Pain and inflammation are intimately correlated. When the body perceives painful stimuli, it incites an acute immune response as a protective measure. Conversely, chronic inflammation, which is provoked by an abundance of external factors, can result in pain. Long-lasting, low-grade inflammation can occur when the body mistakenly generates an immune response. CBD can function to ease an overactive immune system, reducing inflammation. Several complex mechanisms allow CBD to accomplish its effects, which include decreasing the number of proinflammatory cytokines, inhibiting inflammatory mediators and increasing T-regulator cells, which facilitate in suppressing the immune response. Cannabinoid receptors have been found on immune cells, but CBD also works with other pathways in the body to regulate hyperactive immune responses.
Pain is an umbrella term, meaning many conditions are characterized by chronic pain. CBD has been shown to benefit people who experience conditions such as migraines, fibromyalgia, irritable bowel syndrome and arthritis, to name a few. In addition to decreasing inflammation, which can be the root cause of daily anguish, CBD tackles pain pathways head on. Specifically, it acts on vanilloid receptors, which control pain perception, inflammation and body temperature. It also targets serotonin pathways, which influence mood, hunger, sleep and pain. Cannabinoid receptors are present in areas of the brain that play a role in nociceptive processing and they are also found in the peripheral nervous system, which senses painful stimuli.
CBD can be administered as an oil (which is a phytocannabinoid extract in a carrier oil, such as coconut or olive oil) for systemic relief as well as topically to target localized discomfort. Using CBD is just one tool in the practitioner’s toolbox to help mitigate pain. Integrating CBD with other holistic modalities can optimize pain relief.
Dietary changes
Changing eating habits from the “Western pattern diet” is a critical component in lowering inflammation. Following an anti-inflammatory food plan by reducing or eliminating foods that contribute to inflammation and increasing foods that lower inflammation is foundational for health and wellness. A diet high in processed food, refined carbohydrates, added sugars and fried items is considered proinflammatory by integrative and functional nutritionists. Gluten, a protein found in wheat, rye, barley and other grains, can also contribute to inflammation, as can other grains that do not contain gluten. Seeking the advice of a registered dietitian nutritionist to guide your food plan is essential to reducing pain and inflammation.
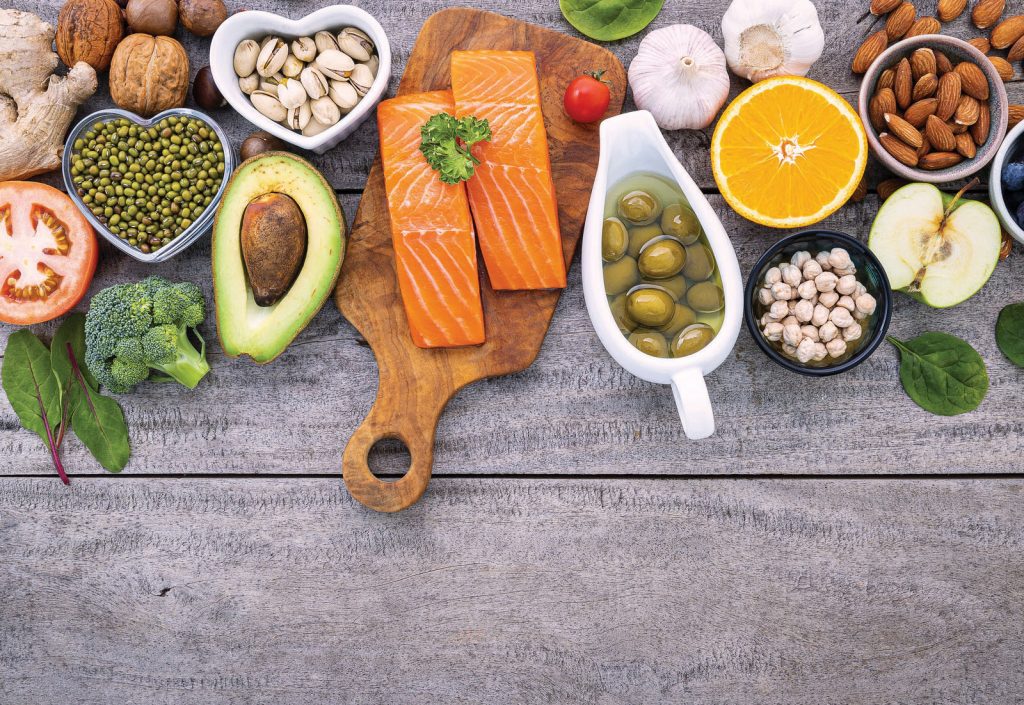

What foods are recommended?
A diverse food plan full of nutrient-dense whole foods can help to reduce inflammation, optimizing health. Vegetables and fruits contain phytonutrients, which have potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Incorporating foods such as dark leafy greens and berries can increase vitamin and mineral intake, providing the nutrients needed to quell inflammation. Restorative fats such as avocado, coconut and olive oil can support immune health, especially through their positive effects on the gut. Studies have shown that a compound in olive oil called oleocanthal has effects similar to those of ibuprofen.
Omega-3 fatty acids are also essential to consider in the inflammatory process. The primary source of these is fatty fish, such as salmon. Although flaxseeds, pumpkin seeds, hemp seeds and walnuts contain omega-3s, the amounts are not as significant or as bioavailable as those from fish. When buying fish, stick to non-predatory, high-quality fish to avoid exposure to heavy metals, another environmental trigger of inflammation. Botanicals in the form of herbs and spices, such as black pepper, cayenne, cinnamon, clove, fenugreek, garlic, ginger, mustard seed, onion, rosemary, thyme and turmeric, have all been shown to contribute to reducing inflammation.
Additional tools
Cannabis and anti-inflammatory foods are just the beginning when it comes to building a foundation to manage pain. Add stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation, yoga and deep breathing, to decrease stress-induced inflammation. An infrared sauna can help to promote the removal of toxins that can contribute to inflammation. An integrative approach including CBD, an anti-inflammatory food plan and stress-reduction techniques may reduce pain, improving quality of life. Along with reducing pain, these suggestions can also boost mood, optimize brain function, stabilize sleep patterns, improve gut health and decrease the risk of developing certain chronic diseases.
Laura Lagano, MS, RDN, CDN, (https://lauralagano.com/)is an integrative and functional nutritionist and a holistic cannabis practitioner. Laura is the co-founder and education director of the Holistic Cannabis Academy (https://holisticcanna.com), an online learning platform about integrating cannabis/CBD with nutrition and other holistic healing modalities. You can reach Laura at laura@lauralagano.com.